In early 2022, Ripple proposed a novel automated market maker (AMM) design for the XRP Ledger. It has subsequently been implemented on a devnet, with a mainnet launch being contingent upon governance approval of a proposal that will be shared at a later date.
Unlike traditional blockchain-based AMMs (such as Ethereum-based AMMs), it integrates directly into the XRPL itself as a core primitive. This makes it a fundamental building block of the XRP Ledger and supports Ripple’s goal of providing XRPL developers with the resources and tools needed to grow the ecosystem.
It’s worth noting that the XRPL is an open-source blockchain that is independent of Ripple, with Ripple managing approximately 4% of validators.
In this article, I will provide a high-level overview of this new AMM. In particular, I will explain five key features that distinguish it:
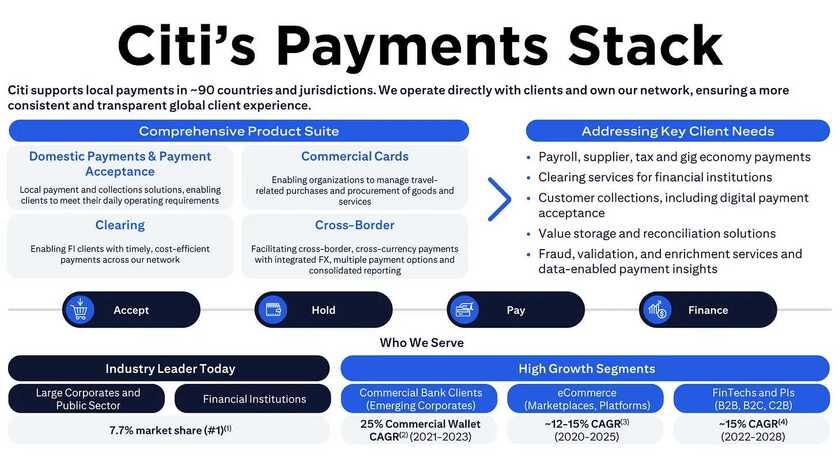
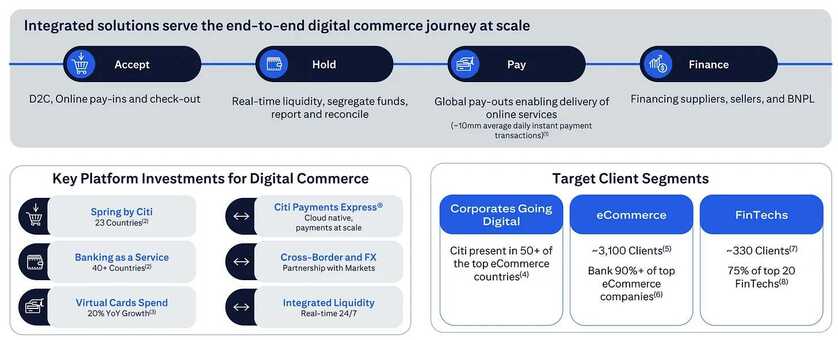
- Protocol-Native AMM: protocol-wide liquidity pools mean that liquidity is shared at a blockchain level. This makes it easy for developers to integrate AMM functionality into their projects, removing pain points such as liquidity bootstrapping.
- No MEV or Front-Running: federated consensus and canonical transaction ordering eliminate MEV and front-running. Both terms will be explained in detail below.
- Single-Sided Liquidity Provisioning: most liquidity pools require 2 tokens to be deposited at a 1:1 ratio. The XRPL’s AMM requires only a single asset, with the protocol automatically swapping the token in order to maintain a 1:1 ratio.
- Central Limit Order Book Integration: both AMM pricing and order book pricing are enabled on the XRPL, with the best price being automatically executed for users.
- Continuous Auction: arbitrageurs may bid for 24-hour trading slots for the AMM with near-zero fees, allowing them to immediately bring prices back to equilibrium with external markets and resulting in greater profitability. Liquidity providers are also compensated through the distribution of winning bid amounts for each AMM pool, mitigating impermanent loss exposure.
Below I’ll explain each in-depth, and do my best to provide an opinion on the validity of each idea.
A Protocol-Native AMM
One of the biggest challenges faced by decentralized exchanges (DEXs) is attracting liquidity. Therefore, it’s common for DEXs (who typically rely upon AMMs for pricing) to offer liquidity incentives in the form of high APRs in order to bootstrap liquidity for their liquidity pools. While effective at attracting liquidity, it also frequently results in mercenary capital that’s quick to leave as soon as the rewards drop, harming long-term sustainability. Liquidity is a project’s lifeline in DeFi and attracting it is a top priority, but attracting it requires high capital investments for initial bootstrapping and fragmentation between projects.
The XRPL’s new AMM is protocol-native, meaning that it’s built at the blockchain level itself with protocol-wide liquidity, despite varying front-facing interfaces. There may only be one pool per asset pair, and anyone may create a new XRPL liquidity pool.
The result is that those building on the XRPL can integrate their own DEX/AMM interfaces in order to add swap functionality, without requiring liquidity to be bootstrapped nor being at risk of mercenary capital or high slippage.
A drawback to this is that it appears AMMs may no longer be able to differentiate themselves based on factors such as having low slippage or a wide selection of assets. However, this could also be seen as an improvement as it lets developers focus on more important innovations without needing to commit resources to attracting AMM liquidity. For example, XRPL developers could now focus on vertical integration with the XRPL by adding other products such as their own stablecoin and borrowing/lending markets.

No MEV or Front-Running
Front-running is one form of miner extractable value (MEV) whereby a profitable transaction is seen in the mempool and the same trade is made, albeit with a higher gas fee so that it is executed first. Given the speed at which blocks are created, this is most commonly performed by bots. For example, if I were to discover a profitable trade for $10 and look to execute it, a bot could execute it before me by paying more in gas fees, and take off with the profit.
Various groups such as FlashBots are actively studying MEV and it is estimated that the gross extracted value on Ethereum alone has exceeded $700M. While not all MEV is bad, it’s become clear that substantial value has been taken away from users.
The XRPL eliminates MEV and front-running through the following:
Federated Consensus
With federated consensus, only a subset of validator nodes must come to consensus which significantly increases throughput. Stellar also uses this design with their subsets of nodes being referred to as quorum slices, whereas with the XRPL the subsets are referred to as Unique Node Lists (UNLs).
Certain default UNLs are available for new node operators, with these default lists being formed based on successful past performance, having proven identities, and having stringent IT standards. Despite this, other UNLs may be proposed and/or chosen as desired. In general, underperforming nodes are removed as the UNLs are updated, meaning that over time the top nodes are rewarded. The result is that a group of validators come to a consensus about a given block’s transactions, so there is no single validator prioritizing transactions based on gas fees.
Canonical Transaction Ordering
Validators in PoS blockchains are incentivized by profit and as such they prioritize transactions with the highest associated gas fees, opening up the potential for MEV.
Instead, canonical transaction ordering means that transactions are ordered in a deterministic way that is hard to predict, while all network nodes still agree on the order of transactions. The inability to predict transaction ordering means that front-running potential is either severely mitigated or outright eliminated.
Are the above effective?
Some argue that federated consensus is not truly decentralized as validators are assigned by default. I agree as this appears to be default bias, but I’m also not a maxi that everything needs to be fully decentralized at all times. However, the number of validators managed by any single entity is limited, such as Ripple having only 2 of 35 validators. While not as decentralized as Ethereum per say, I appreciate the benefits conferred by this methodology and note the stringent UNL requirement. I’m of the opinion that the validators are worthy of their positioning despite the default bias, but also appreciate concerns over this.
Single-Sided Liquidity Provision
Liquidity pools most commonly contain a given pair of assets, such as XRP and USDC. In order to help maintain an equal composition between the two, new liquidity providers must typically provide both assets in equal proportions, such as $50 in value for each. This causes friction for liquidity providers, as they must first swap assets to have equal proportions of each, or otherwise be limited to depositing the lesser amount of either asset held.
The XRPL’s AMM enables liquidity providers to deposit only a single asset into a given pool, with half of the asset’s value being automatically converted into the paired asset. For example, if one wished to deposit $100 of XRP into a USDC/XRP pool, 50% of the XRP would be automatically converted to USD and both would then be deposited in equal amounts.
I’m very supportive of this idea and see it as the next step in the evolution of not only DEXs, but DeFi itself. I first saw this idea while working on the Venus Protocol V4 whitepaper, where it was detailed how back-end integration with Pancake Swap would enable anyone to borrow/lend the assets of their choice. If I were to only have USDC but wanted to lend another asset, Venus would automatically swap it while taking 25% of the swap fee.
This idea significantly improves user experience and I see DeFi moving heavily toward this in the future. It’s great to see the XRPL already integrating it.
One question that comes to mind, however, is in regards to new liquidity pools comprised of long-tail assets. I imagine that as liquidity providers deposit these assets which may then be swapped automatically, they could be subject to moderate slippage. That being said, this is only theoretical and likely has been thought through already.

Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) Functionality
To date, the XRPL has solely used a CLOB design, which is common in traditional finance and has orders executed based on matching buy/sell orders. On the XRPL, the limit orders are referred to as offers and these offers may be either partially or fully filled. Additional functionalities such as auto-bridging exist, where trades automatically use XRP as an intermediary token should it be cheaper than trading directly token-to-token.
While this is well-suited to the XRPL, most decentralized exchanges rely upon AMM pricing and each approach has its unique strengths and weaknesses. For example, order books tend to require greater liquidity (and therefore market makers with ample funds). The XRPL’s new AMM on devnet now incorporates both models and extracts liquidity from both, thus providing the best pricing with the least slippage.
I imagine that optimal pricing would typically be via an AMM but that order book functionality would at times be beneficial (e.g. limit order trade functionality). It may be especially helpful for providing liquidity within certain trade bandwidths, in a similar fashion to Uniswap’s concentrated liquidity. Rather than relying upon AMM pricing, a heavy build-up of order book trades may help cushion any slippage impact.
Continuous Auctions
Arbitrageurs wish to profit from price discrepancies between decentralized exchanges, meaning that they’ll compete with others to execute trades where profits outweigh any potential transaction costs incurred. These transaction costs can be high on certain blockchain networks and subject to inefficiencies caused by slow block speeds.
On the XRPL, transaction costs are low and block speeds are fast, meaning that arbitrageurs can immediately bring prices back to equilibrium with external markets. This is especially relevant during highly volatile periods, as fast trade execution enables greater profitability.
However, arbitrageurs aren’t the only party to benefit from the XRPL’s architecture. One common challenge for liquidity providers is that asset price discrepancies lead to impermanent loss, a form of opportunity cost due to price divergence. For example, if XRP and USDC were to diverge in price, liquidity providers may have benefitted more by simply holding XRP instead of providing it as liquidity.
The XRPL mitigates the above through a continuous auction process where arbitrageurs bid for 24-hour windows during which they’re subject to near-zero trading fees. As XRPL transaction fees are already minimal, this is especially relevant to any arbitrageur executing a high number of trades. If another party were then to outbid them, they would be refunded pro rata. Therefore, we can expect that bids are based on historical data and any personal analysis + bias. Bid amounts that are processed are distributed amongst each AMM pool, in turn compensating liquidity providers and mitigating impermanent loss.
In summary, each liquidity pool has a 24-hour window during which arbitrageurs may bid for the right to near-zero trading fees. The bids reward liquidity providers, while arbitrageurs can efficiently capture any price discrepancies which in turn mitigates impermanent loss further.
It’s hard for me to comment on how this would work in practice as I’m missing some detailed quantitative information, and it’s such a novel idea I haven’t dug into before. For example, as more users arrive at the XRPL and arbitrage competitiveness increases substantially…will bids become very large? Will this meaningfully compensate liquidity providers? Will impermanent loss be materially mitigated? It seems like yes in theory but it’s hard to tell.
Concluding Thoughts
The XRPL has an advanced technical front but network effects are huge in DeFi. While Ethereum/BSC/Tron currently have ~80% of TVL, the XRPL is adding new capabilities that will drive further adoption and grow its developer community. For example, it recently added NFT capabilities, and additional features such as interoperable sidechains, portable digital identities, and smart contracts are expected later this year.
On the technical front, the new XRPL AMM is very low-cost, fast, and sustainable which are all great characteristics of a blockchain ecosystem. If they are able to build out a strong developer community, attract TVL, and address real-world challenges, they will be well poised. In fact, former colleagues of mine shared great things after attending the XRPL’s Apex Summit last year in Las Vegas, and an upcoming one in Amsterdam this September. Meeting the projects in-person tends to be very effective in evaluating an ecosystem.
In the meantime, I hope that the above piece was able to shed light on key architectural differences that distinguish the XRPL from others. The AMM is currently in the devnet stage but will be available in the coming months, and it should be an exciting time.









 All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.
All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.