NEW FED PAPER: "...the technology associated with tokenized platforms is not incompatible with existing central bank money functioning as a settlement asset." Translation: paper concludes no need for the Fed to issue a wholesale CBDC as a new settlement asset. ~Kaytlyn Long
Abstract
This paper explores whether a new settlement asset in the form of central bank money is essential for a new platform that processes wholesale payment transactions. Central bank money currently exists for wholesale transactions in the form of depository institution balances at the Federal Reserve (Reserve Banks) used for Fedwire® Funds Service (Fedwire).2 Increasing public-sector experimentation with and private-sector usage of distributed ledger technology (DLT) for the transfer of value has led many to ask whether the existing form of central bank money can be used as a settlement asset in DLT transactions. Examining the key technological characteristics and potential arrangements of tokenized distributed platforms and comparing them with existing settlement assets, transfer mechanisms, and balance sheet entries, we argue that a new settlement asset in the form of central bank money is not essential for a tokenized wholesale payment system.
Introduction
Recently there has been a renewed interest in wholesale central bank digital currency (wCBDC).3 For the purposes of this paper, wCBDC is defined as a potential new form of central bank money and a digital liability of a central bank that is only accessible by eligible entities, such as depository institutions (DIs), which purportedly could allow for new technical capabilities and arrangements in interbank payments, clearing, and settlement, including use of tokenized platforms, programmability, and composability.4 Since CBDC implies a new form of money, using the term "wholesale CBDC" suggests that a new central bank liability is essential to achieve these purported benefits.5 In order to be distinct from existing central bank money, a new central bank liability would need to have a different legal structure and be recorded on the central bank balance sheet separately from the DI balances held in master accounts.6 However, providing a central bank liability to DIs is not itself a novel activity since DIs currently have access to central bank money in a digital form. And in payments terms, attributes like tokenization are related to the platform, or transfer mechanism, of a payment, not to the settlement asset itself.
It is therefore important to ask whether a new settlement asset, specifically new central bank money, is essential for a new transfer mechanism for wholesale payment transactions. For the purposes of this note, we limit the question to whether a new central bank liability/new settlement asset is necessary to facilitate payments on a new technology platform. Other policy questions may have different discussions about the need for a new liability to achieve those policy objectives. This paper first provides a simple framework for thinking about central bank money and wholesale payment systems. It then provides an overview of today's wholesale payment systems that settle in central bank money. Next, it provides an explanation of the technology attributes and arrangements associated with a new payments platform to determine whether these attributes and arrangements are incompatible with the existing settlement asset. Finally, the paper examines whether a new form of central bank money (a new settlement asset) may be needed for a new wholesale payment system (a new transfer mechanism).
Simple Framework for Central Bank Money and Wholesale Payment Systems
Central Bank Money
Central bank money is a liability of the central bank. It may take the form of physical currency that is widely available to the general public or the form of digital balances held by DIs and other eligible institutions at central banks.7 The term "reserves" is commonly used to describe these digital balances held by DIs, and footnote 4 of the H.6 Release (Money Stock Measures) defines reserves balances as "balances held by depository institutions in master accounts and excess balance accounts at Federal Reserve Banks."8
From a payments perspective, central bank money in master accounts is used as a settlement asset for Federal Reserve Financial Services (FRFS).9 A settlement asset (the "what") is used to discharge obligations as specified by the rules and regulations for a financial market infrastructure.10 Since central bank money has neither credit nor liquidity risk, it is considered the safest form of money.11 The settlement asset aspect of central bank money is important when discussing CBDC because the Federal Reserve has other liabilities on its balance sheet that do not function as settlement assets, such as overnight reverse repurchase agreements. Given the expectation that it will be able to transfer value, CBDC as a new form of central bank money should be viewed as both a liability of the central bank and as a settlement asset.
Wholesale Payments
Wholesale payments are defined by certain attributes: They are typically thought of as transactions between DIs or other eligible financial institutions and as being large-value payments. Fedwire is one example of a wholesale payment system or transfer mechanism (the "how").12 For the purpose of this analysis, any new wholesale payments system would be transferring large-value payments between eligible institutions.13 Any institution that currently can access and use the existing wholesale payment system would be eligible to connect to a new wholesale payment system. However, in this analysis, institutions that do not have access to the existing system would not have access to the new system, either.14
Simple Framework for Analysis
A simple way to separate the benefits of a new central bank liability that functions as a settlement asset – the what – from the benefits of transfer mechanism or payments platform – the how – is to identify the potential states that may exist for settlement assets and platforms. As seen in table 1, there are four potential states derived from whether there is a new or existing liability that is a settlement asset and a new or existing payments platform that is used as a transfer mechanism. For simplicity, we will refer to the existing liability functioning as a settlement asset as “reserves” rather than the “balances held by DIs in master accounts.” The existing centralized wholesale payments platform considered in this analysis is Fedwire. Because the potential for new technical capabilities is a motivating factor in discussing a wCBDC, this analysis considers the new theoretical platform to be a “tokenized” distributed platform that may use new technology such as distributed ledger technology (DLT).15 However, the framework could be applied to any new wholesale transaction platform and does not require transaction ledger-keeping to be distributed or decentralized.
Table 1: Simple Framework for Analyzing Central Bank Money and Wholesale Payment Systems

The top left quadrant shows the status quo for wholesale payments with central bank money: reserves transferred on an existing platform such as Fedwire. The top right quadrant shows that keeping the existing liability/settlement asset and moving to a new platform would create a system that looks like reserves on a tokenized distributed platform. However, not until a new liability is introduced on the bottom row does the concept of wCBDC, as defined in this paper, get introduced. That new row shows two possible versions of wCBDC, one version of a new liability/settlement asset that uses a new platform and one that does not. This difference serves as a reminder that simply introducing a new liability/settlement asset does not guarantee the benefits associated with a new platform. Definitionally, within this framework, for one to actually use the term wCBDC as a means for tokenization, programmability, and composability, one would need both a new liability/settlement asset and a new payments platform (bottom right quadrant).
These distinctions are important in determining what exactly is being created and where the new potential benefits are coming from. If the benefit were solely from the liability, then a comparison of existing payments platforms, one with a new settlement asset and one using reserves, should demonstrate material differences between a transfer on the two wholesale platforms (holding other policy issues like operating hours and access constant). In other words, if benefits were from the liability, a transfer that uses a new central bank liability on Fedwire should demonstrate differences from a transfer that uses reserves on Fedwire. If, instead, benefits stem from moving to a new payments platform, what benefits does the new liability contribute? Are there reasons not to use reserves on a new payments platform? These are the questions this paper seeks to address in subsequent sections.
Defining the Status Quo: Existing Wholesale Systems with Central Bank Money
Overview
To understand whether a new form of digital central bank money is essential, it is necessary to recognize how existing wholesale transactions are processed using central bank money as a settlement asset. More than twenty Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructure jurisdictions have a large-value payment system (LVPS) that is operated by the central bank.16 Generally, an LVPS is defined as a funds transfer system that handles large-value and high-priority payments using real-time gross settlement (RTGS) or an equivalent mechanism to settle in central bank money.17 For the purpose of this analysis, we use Fedwire as our example, an RTGS system that enables participants to make payments with immediate finality through credit transfers using their balances held at Reserve Banks or intraday credit provided by those Reserve Banks (that is, by using what would be considered central bank money in either case). We focus on the settlement asset (central bank money), how the transfer of value appears on the Federal Reserve's balance sheet (accounting treatment), and the transfer mechanism itself (payments platform).
Liability/Settlement Asset: Central Bank Money
Federal Reserve Operating Circular (OC) 1 sets forth the terms under which a DI is eligible for a master account (including opening, maintaining, and terminating an account) and financial services with its Reserve Bank and describes the tools that an account holder may use to segregate, report, and settle debit and credit transaction activity in the master account. OC Section 6 explains that a master account is used to settle debit and credit transactions that the DI conducts with or through any Reserve Bank. Funds in the master account, which are assets of commercial banks and liabilities of the central bank, are the payments platform's settlement asset. Every Fedwire participant must maintain a master account at the Federal Reserve.
Federal Reserve Balance Sheet
According to the 2023 Financial Accounting Manual for Federal Reserve Banks, each Reserve Bank sets up "a general ledger and subsidiary accounts as it requires for its own purposes to prepare the balance sheet and to maintain satisfactory internal controls."18 The line item for the deposits of depository institutions is 220-025. These deposits are balances maintained by DIs in accounts at Reserve Banks. "Depository institutions may hold balances in master accounts, excess balance accounts, and temporary transitional accounts. Depository institution balances in all of these accounts are captured in this line item."19 Since the balance sheet is organized by the holder, no distinction is currently made between types of accounts.
Transfer Mechanism (Platform)
Regulation J and OC 6 consist of rules regarding funds transfers over Fedwire.20 For a DI to use a wholesale payment system like Fedwire, it must maintain a master account and hold central bank money in its account at the Federal Reserve. The payment instructions are for the delivery of "central bank money," and once the payment is processed, Reserve Banks debit the account of the sending DI and credit the account of the receiving DI. Funds are ultimately settled on the books of the Federal Reserve and thus are settled in central bank money. From an operational standpoint, many of the actions that the Reserve Banks perform as sending or receiving banks in a funds transfer are accomplished by Fedwire.21
New "Tokenized" Distributed Payments Platform: Technology and Arrangements
To determine whether the technology associated with tokenized platforms is incompatible with reserves as a settlement asset, it is necessary to identify key characteristics of the technology. Early permissionless crypto-asset distributed value-transfer systems, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, were conceived to create a system where anyone may participate, and participants are incentivized to act in a way that is consistent with the system operating as intended. In addition, the system is designed to minimize the impact of dishonest participation. The scholarship on decentralized and distributed value-transfer systems shows that the key characteristics of these platforms for value-transfer systems include (1) strong proofs of funds ownership through asymmetric cryptography, (2) prevention of double-spend through consensus mechanisms, and (3) ability to program money to execute specified logic.22
Strong proofs
Foundational to these technologies is the implementation of asymmetric cryptography to support a variety of purposes, but two primary uses stand out: strong proofs of funds ownership and authorization of payments. 23 This usage of cryptography in permissionless platforms differs from practices in traditional systems that represent ownership through relational databases and tables, which consequently break up authorization (for example, username and password, secure API gateways) and ownership (for example, a ledger maintained and owned by a single entity) into discrete steps.24 Theoretically, in a tokenized world, whoever holds the private key owns the asset and is the sole authorizer.
Prevention of double-spend
In any value-transfer platform, double-spend (that is, the threat of spending the same funds twice) must be prevented to ensure the validity of the payment platform. The combination of technical components and economic incentives to prevent double-spend is one of the foundational aspects of a crypto-asset system because it allows for trust to be distributed across the system's design without relying on a single, centralized actor. Consequently, the distribution of trust allows for the ownership and authorization of value transfers described above to be trusted.25 This trust model differs from centralized systems that are operated by a single or set of trusted entities. These arrangements do not necessarily require solutions as complex as those described above because prevention of double-spend can be ensured by the trusted operator(s) of a system.
Programming money
The third characteristic identified is the ability to program money to execute in a specific way (colloquially termed "programmability"). While this function is not necessarily new, as product offerings like automated payments are available for traditional deposit products, the implementation of programmable features within crypto-asset systems themselves are novel. One way to think about the difference between programmability in these systems versus traditional systems is to answer the question "How does each respective system provide certain guarantees?" In traditional payment systems that decouple programmable actions (for example, automated transfers at specified days), a central system operator or a group of system operators provides the guarantee that specified logic will be executed.26 In contrast, successful crypto-asset ecosystems leverage cryptographic proofs for ownership, authorization, and distribution of trust to ensure specified programming logic is executed without relying on a central or group of operators to execute. If programmability is necessary for the transfer of value, there may be arguments for ensuring that it is tethered to the settlement system.27
New Technology Brings New Arrangements (and New Risks)
New technology also allows for the design of new arrangements. The decentralization often associated with these technologies allows for the removal of intermediaries, and therefore new payment arrangements often accompany new technology options. As a result, who controls the ledger for decentralized systems may be very different from who controls the ledger for centralized systems.28 Additionally, centralized financial systems generally do not allow just any member of the public to be able to build new products on their technology stack. By design, decentralized systems can allow, and frequently encourage, anyone to build products on top of their settlement layer. As a result, bilateral arrangements that currently exist off the payments platform may be brought on the platform through programmability.
These differences in settlement arrangements and development of the technology stack may introduce new risks into the payment system. For example, operational risks may be introduced in settlement arrangements with a greater degree of decentralization since decentralized governance associated with decentralized platforms often makes it difficult to act quickly when there are operational issues.29 Moreover, lowering barriers to entry for programmability may increase the number of bilateral credit arrangements and atomically settled transactions on the platform.30 However, the existing crypto-asset ecosystem has shown how new applications built on decentralized settlement platforms can introduce liquidity risk into the system.31
From a central bank perspective, these risks can be both to the payment systems themselves and to the reputation of the central bank. To understand scenarios where new central bank money may be essential for a new wholesale payments platform, one must understand the potential for new arrangements to introduce new risks and the ways that such risks need to be sequestered from other central bank transactions.
New Liability/Settlement Asset: Is New Central Bank Money Essential?
Having identified key technological features and potential arrangements of tokenized platforms, we now ask whether a new form of central bank money is essential as a settlement asset in these systems. Addressing that question comprises questions both of operational feasibility and of potential new risks posed to existing settlement assets and payments platforms. We argue that neither the key technological features of a tokenized platform nor the potential arrangements associated with a tokenized platform necessitate a new central bank liability.
Does the Balance Sheet Necessitate New Money?
From a technological feasibility standpoint, reserves should be able to be used on a new "tokenized" platform and a new liability would not be required to achieve the benefits of new technical capabilities. The specifications set out in OC 1 regarding debiting and crediting master accounts held at Reserve Banks should not prohibit master accounts from being used as a central bank liability for a tokenized platform that has strong guarantees, prevents double-spend, and is programmable. DIs could still hold reserves in master accounts at the Reserve Banks, which are then debited and credited with other DI master accounts through a new tokenized platform. Since the accounting line item 220-025 currently can be used for different types of accounts, including master accounts, there is no obvious reason it could not be used for recordkeeping on the general ledger.32 It is also important to note that the language of accounts, balances, and debit/credit are not inherently incompatible with the notion of tokenization and thus the data structure for accounting does not itself suggest the need for a new liability rather than a tokenization approach.33
Does New Technology Necessitate New Money?
The same beneficial attributes DLTs can provide to a payment system, such as strong proofs of ownership and payment authorization, double-spend prevention, and programmable money, could also create new payment system risks. For example, errors in a smart contract's programming or technical flaws in a new arrangement between DIs (for example, lending arrangements) may add to or enhance credit and liquidity risks within the payment system. More specifically, if the ability to program money lowers the barrier to entry for activities that traditionally occur outside the payment system, bringing them onto the payment system may introduce more risk to the central bank.
Nevertheless, the risks associated with new technology may not create a need for a new type of central bank money. Depending on who has certain authorities within the payment system, these new risks could be mitigated. For example, contingent on its level of control, the central bank could install a risk-management practice akin to those on its other payment systems. This approach leads to the question of not what the technology is, but who has the potential to mitigate the risks that the system design may introduce. For the purposes of new risk, it seems that the technology itself would not create a need for a new version of central bank money.
Do New Arrangements Necessitate New Money?
If it is not the risks themselves, but instead the ability to mitigate the risks that is the crux of whether there is a need for a new form of money, the arrangement of the new payment system becomes vital. Some CBDC projects, both international collaborations and private-sector initiatives, envision a world where a jurisdiction's CBDC runs on a payments platform operated by a group of central banks or a private entity. Additionally, some proponents of CBDC describe the ability for the private sector to build on top of the central bank's technology stack, specifically on top of the settlement layer, as a key potential innovation that a CBDC-based financial system could bring.34
Since it is technically feasible to use reserves for a new payments platform, if the Federal Reserve operates the new payments platform and prohibits private-sector development on the technology stack, the payment system could be thought of as just another digital FRFS product or service, along with Fedwire, FedACH®, and FedNow®.35 In this case, the Federal Reserve should be able to conduct risk management and oversight in the same way that it does with its other services. As a result, reserves should be able to be used as a settlement asset on a new payments platform, and there is no compelling reason to issue a new central bank liability.
Other arrangements that include the private sector also do not dictate the need for new central bank money. In a scenario where a private-sector entity operates the payments platform, there would need to be some sort of legal or technical connection between the settlement asset and the platform that would either confer the legal designation of being a central bank liability on a private-sector platform or technically connect central bank accounting systems to a private-sector platform. This type of connectivity does not currently exist in the United States, though other jurisdictions, such as Switzerland, allow for central bank money to operate on a private platform through legal agreements.36 From a technical standpoint, allowing direct private-sector system operational connectivity into reserves introduces a variety of risks, including a new vector for operational risk. Yet, the risks associated with private-sector arrangements likely still have more to do with permitting the activity itself rather than permitting a new form of money. Furthermore, to determine necessity, one would have to identify a circumstance where it not only would be permissible for private-sector activity to access the Federal Reserve balance sheet or platform but also essential that those transactions are not settled with central bank money recorded as 220-025 on the balance sheet. While there may be reasons for wanting to avoid contagion using segregated accounts, there are alternative risk-management practices available to address spillover between systems, making a new form of central bank money unnecessary from a central bank balance sheet perspective.37
More Examination Needed: Possibility of Spillover Due to Private-Sector Products and Services
While new central bank money is not essential for a new payments platform, it is possible that central banks may consider whether circumstances exist where a new central bank liability may be advantageous. One potential circumstance for future examination is when a proposed platform substantially increases risk. For example, there could be a scenario where the central bank manages the new tokenized payments platform but allows institutions to build on top of the infrastructure. Programmability built into the platform may not only create lower barriers to entry for bilateral arrangements between parties, but it may also create additional credit and liquidity risks. For example, a widely used program meant to escrow funds for a particular use case could introduce liquidity risk into the system.38 New credit risk could arise from lending between institutions that would not have otherwise lent but for the programmability feature. Even though DIs, and to an extent central banks, currently manage the risks of these agreements on existing payment platforms, lower barriers to entry may increase the occurrence of these transactions associated with additional risk. If reserves held in master accounts are used for both the new tokenized payments platform and existing payment services, it is possible that liquidity and credit risks could spill over from the new platform to existing ones.
Though this example relies on several assumptions that need to be further explored, it highlights the possibility that introducing private-sector products and services to central bank money could affect the risks in existing central bank payment systems. In such a scenario, the option of a new, separate form of central bank money may be considered by some central banks (though it is certainly not the only option).
Conclusion
Simply using central bank money on a new technology platform does not necessarily make it a new form of central bank money, and the technology associated with tokenized platforms is not incompatible with existing central bank money functioning as a settlement asset. Although the technological features and potential arrangements of tokenized platforms could potentially prove useful, a new settlement asset in the form of wCBDC is not essential for these platforms to transfer central bank money. Should arrangements exist that involve private-sector participants, they may increase risk across all central bank payment services and may therefore require a different type of account. New central bank money is not the only solution, since legal agreements can designate accounts on another payment system as being legally comparable to master accounts. Thus, questions surrounding the necessity of a new settlement asset specifically for wholesale payment transactions should instead be framed as questions regarding risk appetite for how the private-sector can use central bank money.
The Dinarian On Locals is a labor of love that I pour my heart and soul into during my personal time. Countless hours are dedicated to delivering you the most up-to-date, unfiltered, and authentic news and information. Your support means the world to me, and I invite you to consider making a donation or becoming a dedicated supporter of this project. Any amount of XRP donations can be sent to XRP address: rqEy1PDACRg3p9RaVEZz6jU1g9RgguP91 or by scanning the QR code below and are not only appreciated but needed...
To those of you already backing my efforts, I extend my deepest gratitude. Your generosity fuels this mission, and I genuinely thank you from the depths of my heart. Together, we can continue to bring you the best results and make a significant impact in everyones future! ~D

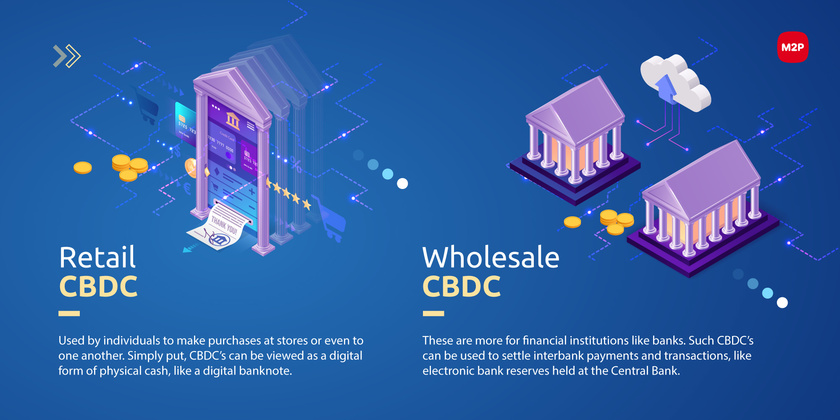








 All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.
All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.