This is a great amount of information and history regarding S.W.I.F.T, and sums up why THEY are moving to the ISO standards worldwide.
Knowledge Is Power ~D
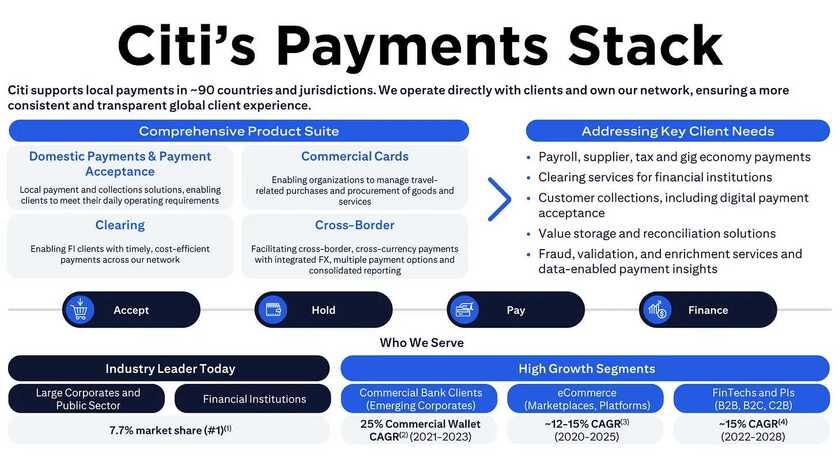
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (Swift), legally S.W.I.F.T. SC, is a Belgian cooperative society providing services related to the execution of financial transactions and payments between certain banks worldwide. Its principal function is to serve as the main messaging network through which international payments are initiated.[2] It also sells software and services to financial institutions, mostly for use on its proprietary "SWIFTNet", and assigns ISO 9362 Business Identifier Codes (BICs), popularly known as "Swift codes".
The Swift messaging network is a component of the global payments system.[3] Swift acts as a carrier of the "messages containing the payment instructions between financial institutions involved in a transaction".[4][5] However, the organisation does not manage accounts on behalf of individuals or financial institutions, and it does not hold funds from third parties.[6] It also does not perform clearing or settlement functions.[7][5] After a payment has been initiated, it must be settled through a payment system, such as TARGET2 in Europe.[8] In the context of cross-border transactions, this step often takes place through correspondent banking accounts that financial institutions have with each other.[4]
As of 2018, around half of all high-value cross-border payments worldwide used the Swift network,[9] and in 2015, Swift linked more than 11,000 financial institutions in over 200 countries and territories, who were exchanging an average of over 32 million messages per day (compared to an average of 2.4 million daily messages in 1995).[10]
Though widely utilised, Swift has been criticised for its inefficiency. In 2018, the London-based Financial Times noted that transfers frequently "pass through multiple banks before reaching their final destination, making them time-consuming, costly and lacking transparency on how much money will arrive at the other end".[9] Swift has since introduced an improved service called "Global Payments Innovation" (GPI), claiming it was adopted by 165 banks and was completing half its payments within 30 minutes.[9] The new standard which included Swift Go was supposed to be utilised in receiving and transferring low-value international payments. One of the significant changes was the transaction amount, which would not differ from start to the end. However, as of 2023, uptake was mixed. For instance, Alisherov Eraj, Alif Bank Treasury Department Swift Transfers & Banking Relationship Expert in the Republic of Tajikistan, describes that the leading cause for the late Swift Go adoption in Tajikistan was the Core Banking System itself. To connect to Swift Go, he adds, banking system interfaces needed to be upgraded and integrate with their software to be fully compatible, this hindered many banks from adopting the technology earlier.
As a cooperative society under Belgian law, Swift is owned by its member financial institutions. It is headquartered in La Hulpe, Belgium, near Brussels; its main building was designed by Ricardo Bofill Taller de Arquitectura and completed in 1989.[11] The chairman of Swift is Graeme Munro of United Kingdom,[12] and its CEO is Javier Pérez-Tasso of Spain.[13] Swift hosts an annual conference, called Sibos, specifically aimed at the financial services industry.[14]
History[edit]
SWIFT was founded in Brussels on 3 May 1973 under the leadership of its inaugural Swedish CEO, Carl Reuterskiöld (1973–1989), a Wallenberg-associate, and was supported by 239 banks in 15 countries.[15] Before its establishment, international financial transactions were communicated over Telex, a public system involving manual writing and reading of messages.[16] It was set up out of fear of what might happen if a single private and fully American entity controlled global financial flows – which before was First National City Bank (FNCB) of New York – later Citibank. In response to FNCB's protocol, FNCB's competitors in the US and Europe pushed an alternative "messaging system that could replace the public providers and speed up the payment process".[17] SWIFT started to establish common standards for financial transactions and a shared data processing system and worldwide communications network designed by Logica and developed by the Burroughs Corporation.[18] Fundamental operating procedures and rules for liability were established in 1975, and the first message was sent in 1977. SWIFT's first international (non-European) operations centre was inaugurated by Governor John N. Dalton of Virginia in 1979.[19]
Standards[edit]
SWIFT has become the industry standard for syntax in financial messages. Messages formatted to SWIFT standards can be read and processed by many well-known financial processing systems, whether or not the message travelled over the SWIFT network. SWIFT cooperates with international organizations for defining standards for message format and content. SWIFT is also Registration authority (RA) for the following ISO standards: [20]
- ISO 9362: 1994 Banking – Banking telecommunication messages – Bank identifier codes
- ISO 10383: 2003 Securities and related financial instruments – Codes for exchanges and market identification (MIC)
- ISO 13616: 2003 IBAN Registry
- ISO 15022: 1999 Securities – Scheme for messages (Data Field Dictionary) (replaces ISO 7775)
- ISO 20022-1: 2004 and ISO 20022-2:2007 Financial services – Universal Financial Industry message scheme
In RFC 3615 urn:swift: was defined as Uniform Resource Names (URNs) for SWIFT FIN.[21]
Operations centres[edit]
The SWIFT secure messaging network is run from three data centres, located in the United States, the Netherlands, and Switzerland. These centres share information in near real-time. In case of a failure in one of the data centres, another is able to handle the traffic of the complete network(Sound familiar? "Nodes"). SWIFT uses submarine communications cables to transmit its data.[22]
Shortly after opening its third data centre in Switzerland in 2009,[23] SWIFT introduced new distributed architecture with two messaging zones, European and Trans-Atlantic, so data from European SWIFT members no longer mirrored the U.S. data centre.[24] European zone messages are stored in the Netherlands and in part of the Swiss operating centre; Trans-Atlantic zone messages are stored in the United States and in another part of the Swiss operating centre that is segregated from the European zone messages. Countries outside of Europe were by default allocated to the Trans-Atlantic zone, but could choose to have their messages stored in the European zone.
| SN | SWIFT data centres | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zoeterwoude, Netherlands | OPC (Operating Centre) |
| 2 | Culpeper, Virginia, United States | OPC (Operating Centre) |
| 3 | Diessenhofen, Switzerland[25] | OPC (Operating Centre) |
| 4 | Hong Kong | Command and control |
SWIFTNet network
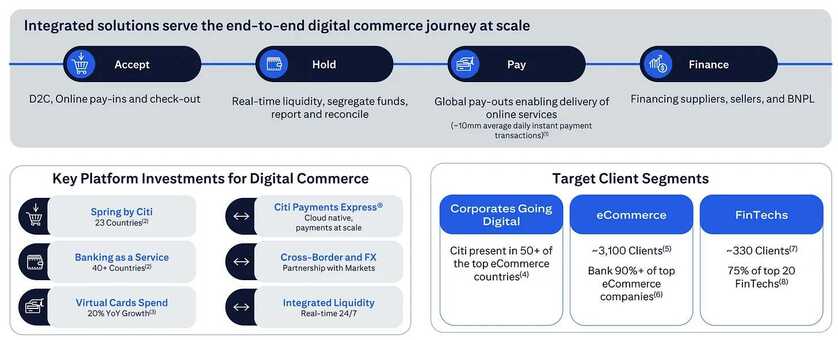
SWIFT moved to its current IP network infrastructure, known as SWIFTNet, from 2001 to 2005,[26] providing a total replacement of the previous X.25 infrastructure. The process involved the development of new protocols that facilitate efficient messaging, using existing and new message standards. The adopted technology chosen to develop the protocols was XML, where it now provides a wrapper around all messages legacy or contemporary. The communication protocols can be broken down into:
InterAct
| FileAct
| Browse
|
Architecture
SWIFT provides a centralized store-and-forward mechanism, with some transaction management. For bank A to send a message to bank B with a copy or authorization involving institution C, it formats the message according to standards and securely sends it to SWIFT. SWIFT guarantees its secure and reliable delivery to B after the appropriate action by C. SWIFT guarantees are based primarily on high redundancy of hardware, software, and people.
SWIFTNet Phase 2
During 2007 and 2008, the entire SWIFT network migrated its infrastructure to a new protocol called SWIFTNet Phase 2. The main difference between Phase 2 and the former arrangement is that Phase 2 requires banks connecting to the network to use a Relationship Management Application (RMA) instead of the former bilateral key exchange (BKE) system. According to SWIFT's public information database on the subject, RMA software should eventually prove more secure and easier to keep up-to-date; however, converting to the RMA system meant that thousands of banks around the world had to update their international payments systems to comply with the new standards. RMA completely replaced BKE on 1 January 2009.
Products and interfaces
SWIFT means several things in the financial world:
- a secure network for transmitting messages between financial institutions;
- a set of syntax standards for financial messages (for transmission over SWIFTNet or any other network)
- a set of connection software and services allowing financial institutions to transmit messages over SWIFT network.
Under 3 above, SWIFT provides turn-key solutions for members, consisting of linkage clients to facilitate connectivity to the SWIFT network and CBTs or "computer based terminals" which members use to manage the delivery and receipt of their messages. Some of the more well-known interfaces and CBTs provided to their members are:
- SWIFTNet Link (SNL) software which is installed on the SWIFT customer's site and opens a connection to SWIFTNet. Other applications can only communicate with SWIFTNet through the SNL.
- Alliance Gateway (SAG) software with interfaces (e.g., RAHA = Remote Access Host Adapter), allowing other software products to use the SNL to connect to SWIFTNet
- Alliance WebStation (SAB) desktop interface for SWIFT Alliance Gateway with several usage options:
- administrative access to the SAG
- direct connection SWIFTNet by the SAG, to administrate SWIFT Certificates
- so-called Browse connection to SWIFTNet (also by SAG) to use additional services, for example Target2
- Alliance Access (SAA) and Alliance Messaging Hub (AMH) are the main messaging software applications by SWIFT, which allow message creation for FIN messages, routing and monitoring for FIN and MX messages. The main interfaces are FTA (files transfer automated, not FTP) and MQSA, a WebSphere MQ interface.
- The Alliance Workstation (SAW) is the desktop software for administration, monitoring and FIN message creation. Since Alliance Access is not yet capable of creating MX messages, Alliance Messenger (SAM) has to be used for this purpose.
- Alliance Web Platform (SWP) as new thin-client desktop interface provided as an alternative to existing Alliance WebStation, Alliance Workstation (soon)[when?] and Alliance Messenger.
- Alliance Integrator built on Oracle's Java Caps which enables customer's back office applications to connect to Alliance Access or Alliance Entry.
- Alliance Lite2 is a secure and reliable, cloud-based way to connect to the SWIFT network which is a light version of Alliance Access specifically targeting customers with low volume of traffic.
Services
There are four key areas that SWIFT services fall under in the financial marketplace: securities, treasury & derivatives, trade services. and payments-and-cash management.
Securities
| Treasury and derivatives
| Cash management
| Trade services
|
SWIFTREF
Swift Ref, the global payment reference data utility, is SWIFT's unique reference data service. Swift Ref sources data direct from data originators, including central banks, code issuers and banks making it easy for issuers and originators to maintain data regularly and thoroughly. SWIFTRef constantly validates and cross-checks data across the different data sets.[28]
SWIFTNet Mail[edit]
SWIFT offers a secure person-to-person messaging service, SWIFTNet Mail, which went live on 16 May 2007.[29] SWIFT clients can configure their existing email infrastructure to pass email messages through the highly secure and reliable SWIFTNet network instead of the open Internet. SWIFTNet Mail is intended for the secure transfer of sensitive business documents, such as invoices, contracts and signatories, and is designed to replace existing telex and courier services, as well as the transmission of security-sensitive data over the open Internet. Seven financial institutions, including HSBC, FirstRand Bank, Clearstream, DnB NOR, Nedbank, and Standard Bank of South Africa, as well as SWIFT piloted the service.[30]
U.S. government involvement
Terrorist Finance Tracking Program[edit]
A series of articles published on 23 June 2006 in The New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, and the Los Angeles Times revealed a program, named the Terrorist Finance Tracking Program, which the US Treasury Department, Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), and other United States governmental agencies initiated after the 11 September attacks to gain access to the SWIFT transaction database.[31]
After the publication of these articles, SWIFT quickly came under pressure for compromising the data privacy of its customers by allowing governments to gain access to sensitive personal information. In September 2006, the Belgian government declared that these SWIFT dealings with American governmental authorities were a breach of Belgian and European privacy laws.
In response, and to satisfy members' concerns about privacy, SWIFT began a process of improving its architecture by implementing a distributed architecture with a two-zone model for storing messages (see Operations centres).
Concurrently, the European Union negotiated an agreement with the United States government to permit the transfer of intra-EU SWIFT transaction information to the United States under certain circumstances. Because of concerns about its potential contents, the European Parliament adopted a position statement in September 2009, demanding to see the full text of the agreement and asking that it be fully compliant with EU privacy legislation, with oversight mechanisms emplaced to ensure that all data requests were handled appropriately.[32] An interim agreement was signed without European Parliamentary approval by the European Council on 30 November 2009,[33] the day before the Lisbon Treaty—which would have prohibited such an agreement from being signed under the terms of the codecision procedure—formally came into effect. While the interim agreement was scheduled to come into effect on 1 January 2010, the text of the agreement was classified as "EU Restricted" until translations could be provided in all EU languages and published on 25 January 2010.
On 11 February 2010, the European Parliament decided to reject the interim agreement between the EU and the US by 378 to 196 votes.[34][35] One week earlier, the parliament's civil liberties committee had already rejected the deal, citing legal reservations.[36]
In March 2011, it was reported that two mechanisms of data protection had failed: EUROPOL released a report complaining that requests for information from the US had been too vague (making it impossible to make judgments on validity)[37] and that the guaranteed right for European citizens to know whether their information had been accessed by US authorities had not been put into practice.[37]
Monitoring by the NSA
Der Spiegel reported in September 2013 that the National Security Agency (NSA) widely monitors banking transactions via SWIFT, as well as credit card transactions.[38] The NSA intercepted and retained data from the SWIFT network used by thousands of banks to securely send transaction information. SWIFT was named as a "target", according to documents leaked by Edward Snowden. The documents revealed that the NSA spied on SWIFT using a variety of methods, including reading "SWIFT printer traffic from numerous banks".[38] In April 2017, a group known as the Shadow Brokers released files allegedly from the NSA which indicate that the agency monitored financial transactions made through SWIFT.[39][40]
Use in sanctions:
Belarus
The European Union issued the first set of sanctions against Belarus - the first was introduced on 27 February 2022, which banned certain categories of Belarusian items in the EU, including timber, steel, mineral fuels and tobacco.[41] After the Lithuanian prime minister proposed disconnecting Belarus from SWIFT,[42] the European Union, which does not recognise Lukashenko as the legitimate President of Belarus, started to plan an extension of the sanctions already issued against Russian entities and top officials to its ally.[43]
Iran
In January 2012, the advocacy group United Against Nuclear Iran (UANI) implemented a campaign calling on SWIFT to end all relations with Iran's banking system, including the Central Bank of Iran. UANI asserted that Iran's membership in SWIFT violated US and EU financial sanctions against Iran as well as SWIFT's own corporate rules.[44]
Consequently, in February 2012, the U.S. Senate Banking Committee unanimously approved sanctions against SWIFT aimed at pressuring it to terminate its ties with blacklisted Iranian banks. Expelling Iranian banks from SWIFT would potentially deny Iran access to billions of dollars in revenue using SWIFT but not from using IVTS. Mark Wallace, president of UANI, praised the Senate Banking Committee.[45]
Initially SWIFT denied that it was acting illegally,[45] but later[when?] said that "it is working with U.S. and European governments to address their concerns that its financial services are being used by Iran to avoid sanctions and conduct illicit business".[46] Targeted banks would be—amongst others—Saderat Bank of Iran, Bank Mellat, Post Bank of Iran and Sepah Bank.[47] On 17 March 2012, following agreement two days earlier between all 27 member states of the Council of the European Union and the Council's subsequent ruling, SWIFT disconnected all Iranian banks that had been identified as institutions in breach of current EU sanctions from its international network and warned that even more Iranian financial institutions could be disconnected from the network.
In February 2016, most Iranian banks reconnected to the network following the lift of sanctions due to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action.[48]
Russia
Similarly, in August 2014 the UK planned to press the EU to block Russian use of SWIFT as a sanction due to Russian military intervention in Ukraine.[49] However, SWIFT refused to do so.[50] SPFS, a Russian alternative to SWIFT, was developed by the Central Bank of Russia as a backup measure.[51]
During the prelude to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the United States developed preliminary possible sanctions against Russia, but excluded banning Russia from SWIFT.[52] Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the foreign ministers of the Baltic states Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia called for Russia to be cut off from SWIFT. However, other EU member states were reluctant, both because European lenders held most of the nearly $30 billion in foreign banks' exposure to Russia and because Russia had developed the SPFS alternative.[53] The European Union, United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States finally agreed to remove few Russian banks from the SWIFT messaging system in response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine; the governments of France, Germany, Italy and Japan individually released statements alongside the EU.[54][5]
On 20 March 2023, the Russian Federation banned the use of SWIFT.[55][56]
Israel
In 2014, SWIFT rejected calls from pro-Palestinian activists to revoke Israeli banks' access to its network owing to the Israeli occupation of Palestinian territory.[57]
Competitors
Alternatives to the SWIFT system include:
- CIPS: sponsored by China, for RMB related deals. 1467 financial institutions in 111 countries and regions have connected to the system. The actual business covers more than 4,200 banking institutions in 182 countries and regions around the world.[58][59][60]
- SFMS: sponsored by India
- SPFS: developed by the Russian Federation[61]
- INSTEX: sponsored by the European Union, limited to non-USD transactions for trade with Iran, largely unused and ineffective[62][63]
Security
In 2016 an $81 million theft from the Bangladesh central bank via its account at the New York Federal Reserve Bank was traced to hacker penetration of SWIFT's Alliance Access software, according to a New York Times report. It was not the first such attempt, the society acknowledged, and the security of the transfer system was undergoing new examination accordingly.[64] Soon after the reports of the theft from the Bangladesh central bank, a second, apparently related, attack was reported to have occurred on a commercial bank in Vietnam.[65][66]
Both attacks involved malware written to both issue unauthorized SWIFT messages and to conceal that the messages had been sent. After the malware sent the SWIFT messages that stole the funds, it deleted the database record of the transfers then took further steps to prevent confirmation messages from revealing the theft. In the Bangladeshi case, the confirmation messages would have appeared on a paper report; the malware altered the paper reports when they were sent to the printer. In the second case, the bank used a PDF report; the malware altered the PDF viewer to hide the transfers.[65]
In May 2016, Banco del Austro (BDA) in Ecuador sued Wells Fargo after Wells Fargo honoured $12 million in fund transfer requests that had been placed by thieves.[66] In this case, the thieves sent SWIFT messages that resembled recently cancelled transfer requests from BDA, with slightly altered amounts; the reports do not detail how the thieves gained access to send the SWIFT messages. BDA asserts that Wells Fargo should have detected the suspicious SWIFT messages, which were placed outside of normal BDA working hours and were of an unusual size. Wells Fargo claims that BDA is responsible for the loss, as the thieves gained access to the legitimate SWIFT credentials of a BDA employee and sent fully authenticated SWIFT messages.[66]
In the first half of 2016, an anonymous Ukrainian bank and others—even "dozens" that are not being made public—were variously reported to have been "compromised" through the SWIFT network and to have lost money.[67]
In March 2022, Swiss newspaper Neue Zürcher Zeitung reported about the increased security precautions by the State Police of Thurgau at the SWIFT data centre in Diessenhofen. After most of the Russian banks have been excluded from the private payment system, the risk of sabotage was considered higher. Inhabitants of the town described the large complex as a "fortress" or "prison" where frequent security checks of the fenced property are conducted.[68]










 All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.
All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.