You cant say I didn't warn you! I have been sending you the link for $GRASS for months now. This is the equivelant to a Theta Staking Node, minus the staking.. for now! You can still get in on this before it goes mainstream and the $GRASS token officially launches mainnet on Solana... ~The Dinarian
What Problem Does Grass Solve?
Over the past few weeks, we’ve been releasing content to explain Grass’s role in the AI stack. As you now know, the protocol performs a number of functions that help builders access web data to train their models with. This is the crucial first stage of the AI pipeline and the launching point for all development.
In Grass’s case, residential devices around the world host a network of nodes that scrape and process raw data from the web. It cleans and converts that data into structured datasets for use in AI training. And most importantly, it sources web data in a way that involves - and rewards - the participation of nearly a million people around the world. It single handedly created the category of AI data provisioning, and it’s the reason some of the largest AI companies in the world have chosen to work with us. It is the Data Layer of AI.
At the same time, we’ve also spent the past few weeks reflecting on the current state of artificial intelligence. We’ve asked ourselves about the most pressing issues it faces, and as a prominent piece of AI infrastructure ourselves, what we can do to solve them.
Our conclusion is that the biggest problem in AI right now is a lack of data transparency. One glance at the news will tell you why. Ask yourself, why would an AI model equate Elon Musk with Hitler? Or erase an entire ethnic group from world history? Was it trained with bad data? Or worse, with good data selectively chosen to give bad answers?
The answer is, we don’t know. And we don’t know because there’s no way to know. We don’t know what data these models were trained on, because no mechanism exists for proving it. There’s no way for users to verify data provenance, because there’s no way for builders to verify it themselves.
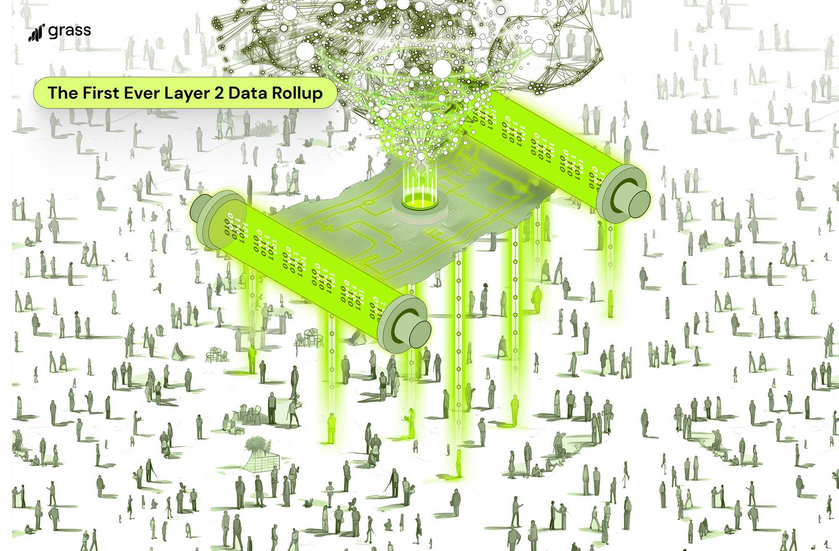
This is the problem that Grass plans to solve, and we’re now building a layer 2 data rollup to solve it. How, you may ask?
Allow us to explain.
How A Layer Two Will Establish Data Provenance
The world needs a method for proving the origin of AI training data, and that’s what Grass is now building. Soon, every time data is scraped by Grass nodes, metadata will be recorded to verify the website it was scraped from. This metadata will then be permanently embedded in every dataset, enabling builders to know its source with total certainty. They can then share this lineage with their users, who can rest easier knowing that the AI models they interact with were not deliberately trained to give misleading answers.
This will be a big lift and involve a major expansion of our protocol as we prepare for scraping operations to reach tens of millions of web requests per minute. Each of these will need to be validated, which will take more throughput than any L1 can provide. That’s why we’re announcing our plan to build a layer 2 solution to handle this significant upgrade to our capabilities. The L2 will be a sovereign rollup, featuring a ZK processor so that metadata can be batched for validation and used to provide a persistent lineage for every dataset we produce. This is what it will take for the base layer of all AI development to advance to the next stage.
The benefits of this are numerous: it will combat data poisoning, empower open source AI, and create a path towards user visibility into the models we interact with every day.
Below, we'll describe the system’s basic design.
The Architecture of Grass
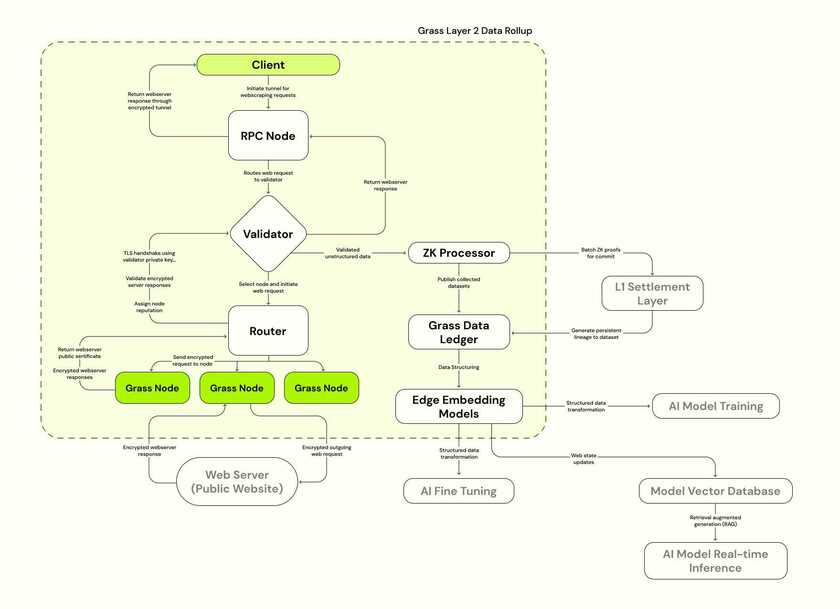
The easiest way to understand these upgrades is by consulting a diagram of the Grass Data Rollup. On the left, between Client and Web Server, you see Grass’s network as it’s traditionally been defined. Clients make web requests, which are sent through a validator and ultimately routed through Grass nodes. Whichever website the client has requested, its server will respond to the web request, allowing its data to be scraped and sent back up the line. Then it will be cleaned, processed, and prepared for use in training the next generation of AI models.
Back in the L2 diagram, you’ll see two major additions on the right that will accompany the launch of Grass’s sovereign layer two: The Grass Data Ledger and the ZK processor.
Each of these has its own function, so we’ll explain them one at a time.
- The Grass Data Ledger
The Grass Data Ledger is where all data is ultimately stored. It is a permanent ledger of every dataset scraped on Grass, now embedded with metadata to document its lineage from the moment of origin. Proofs of each dataset’s metadata will be stored on Solana’s settlement layer, and the settlement data itself will also be available through the ledger. It’s important to note the significance of Grass having a place to store the data it scrapes, though we’ll get to this shortly.
- The ZK Processor
As we described above, the purpose of the ZK processor is to assist in recording the provenance of datasets scraped on Grass’s network. Picture the process.
When a node on the network - in other words, a user with the Grass extension - sends a web request to a given website, it returns an encrypted response including all of the data requested by the node. For all intents and purposes, this is when our dataset is born, and this is the moment of origin that needs to be documented.
And this is exactly the moment that is captured when our metadata is recorded. It contains a number of fields - session keys, the URL of the website scraped, the IP address of the target website, a timestamp of the transaction, and of course the data itself. This is all the information necessary to know beyond a shadow of a doubt that a given dataset originated from the website it claims to be from, and therefore that a given AI model is properly - and faithfully - trained.
The ZK processor enters the equation because this data needs to be settled on-chain, yet we don’t want all of it visible to Solana validators. Moreover, the sheer volume of web requests that will someday be performed on Grass will inevitably overwhelm the throughput capacity of any L1 - even one as capable as Solana. Grass will soon scale to the point where tens of millions of web requests are performed every minute, and the metadata from every single one of them will need to be settled on-chain. It’s not conceivably possible to commit these transactions to the L1 without a ZK processor making proofs and batching them first. Hence, the L2 - the only possible way to achieve what we’re setting out to do.
Now, why is this such a big deal?
Layer Two Benefits
- The Data Ledger
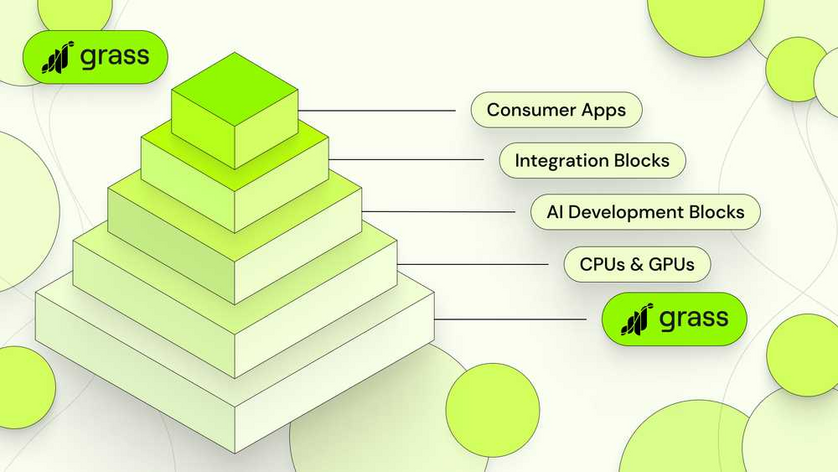
The Data Ledger is significant because it escalates Grass’s expansion into an additional - and fundamentally different - business model. While the protocol will continue to vet buyers who send their own web requests and scrape their own data on the network, a growing portion of its activity will involve the data already stored on the ledger. With this capability, Grass can now scrape data strategically curated for use in LLM training and host it on an ever-widening data repository.
This repository is the data layer of a modular AI stack, from which builders can pick and choose constituent parts to train infinitely differentiated models. It is a microcosm of the internet itself, supplying training data that is already structured and ready to be ingested by AI.
- The ZK Processor
We’ve already gone into a bit of detail about why the ZK processor matters. By enabling us to create proofs of the metadata that documents the origin of Grass datasets, it creates a mechanism for builders and users to verify that AI models were actually trained correctly. This is a huge deal in itself.
There is, however, one piece we didn’t mention earlier.
In addition to documenting the websites from which datasets originated, the metadata also indicates which node on the network it was routed through. Significantly, this means that whenever a node scrapes the web, they can get credit for their work without revealing any identifying information about themselves.
Now, why is this important?
It’s important because once you can prove which nodes have done which work, you can start rewarding them proportionately. Some nodes are more valuable than others. Some scrape more data than their peers. And these are exactly the nodes we need to incentivize to continue the breakneck expansion of the network that we’ve seen over the past few months. We believe this mechanism will significantly boost rewards in the most in-demand locations around the world, ultimately encouraging the people of those locales to sign up and exponentially increase the network’s capacity.
It should go without saying that the larger the network gets, the more capacity we have to scrape and the larger our repository of stored web data will be. A flywheel will inevitably be produced where more data means we’ll have more to offer AI labs who need training data - thus providing the incentive for the Grass network to keep growing.
Conclusion
To summarize, most of the high profile issues with AI today stem from a lack of visibility into how models are trained, and we believe this can be addressed by empowering open source AI with a system for verifying data provenance. Our solution is to build the first ever layer 2 data rollup, which will make it possible to introduce a mechanism for recording metadata documenting the origin of all datasets.
ZK proofs of this data will be stored on the L1 settlement layer, and the metadata itself will ultimately be tied to its underlying dataset, as these datasets are stored themselves on our own data ledger. Grass provides the data layer for a modular AI stack, and these developments will lay the groundwork for greater transparency and rewards for node providers that are proportionate to the amount of work they perform.
This update should help to communicate some of the projects we have on the horizon and clarify the thinking that drives our decision making. We’re happy to play a part in making AI more transparent, and excited to see the many use cases that will arise for our product going forward. These upgrades will open up a wide range of opportunities for developers, so if you or your team are interested in building on Grass, please reach out on Discord. Thanks for your support and do stay tuned.









 All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.
All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.