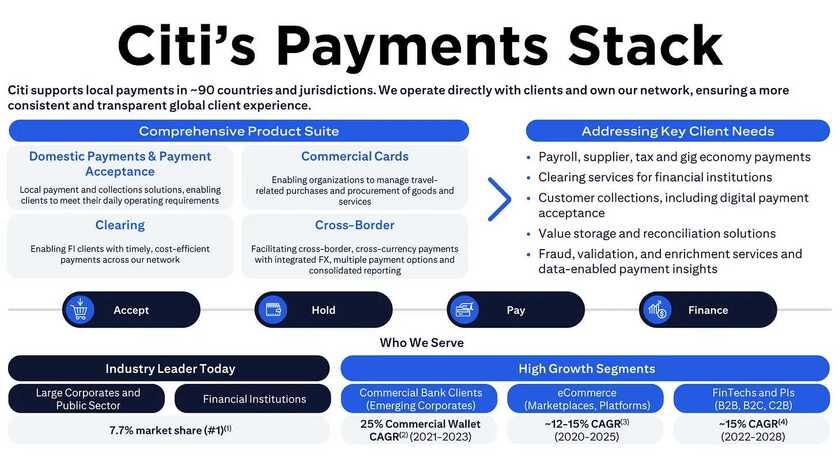
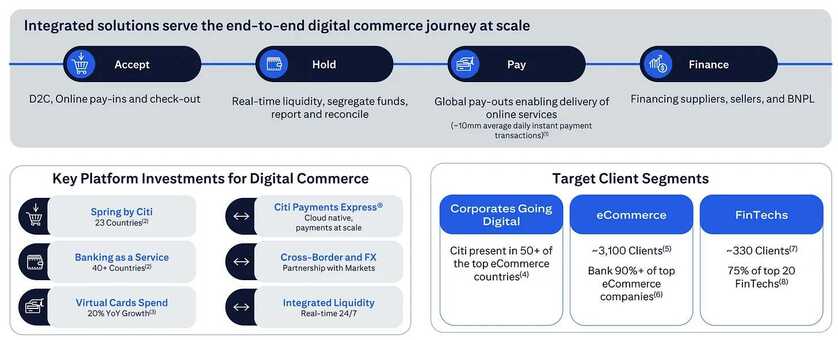
Table of Contents
- Institutional Cross-Border Liquidity
- Two-Tier Monetary Framework
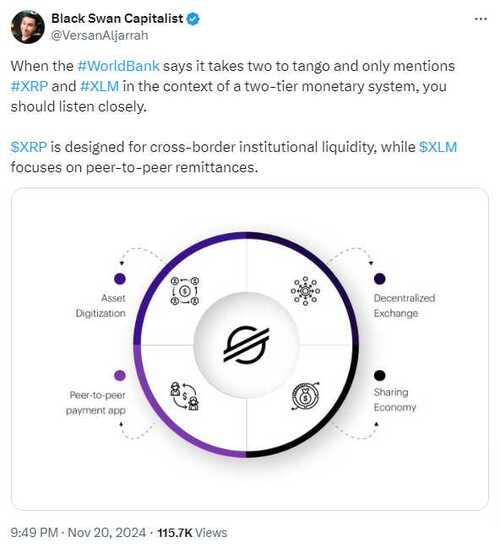
The World Bank and other financial authorities increasingly recognize XRP as a transformative tool for global financial ecosystems.
As Aljarrah noted, XRP is uniquely designed to optimize institutional liquidity for cross-border transactions, a capability that positions it as a crucial asset in a rapidly evolving monetary system. On the other hand, XLM has built a suitable infrastructure to power peer-to-peer transactions efficiently.
Institutional Cross-Border Liquidity
XRP offers a solution to inefficiencies in traditional cross-border payment systems. It eliminates the need for pre-funded accounts, which financial institutions have historically used to facilitate international transactions. Through Ripple’s On-Demand Liquidity (ODL), XRP enables instantaneous currency conversion and settlement, ensuring faster and more cost-effective global transfers.
Two-Tier Monetary Framework
A two-tier monetary system as envisioned by financial experts, positions XRP at the forefront of institutional transactions. In this system, digital assets are used at different levels for specific purposes.
XRP is tailored for wholesale-level transactions, focusing on institutional use cases such as liquidity optimization, whereas Stellar (XLM) is geared toward retail-level remittances and peer-to-peer payments.
The broader adoption of XRP also aligns with the trend of financial tokenization. This process, which converts traditional financial assets into digital tokens, is expected to revolutionize financial systems by increasing transparency and efficiency.
Ripple’s technology is well-suited to support this shift, as its blockchain infrastructure ensures security and compliance with regulatory standards.
Despite the skepticism expressed by some regarding the integration of public cryptocurrencies into central banking systems, the growing adoption of these assets by financial institutions is a testament to their utility.











 All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.
All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.