EVM Chains are the bread and butter of the crypto space. In select cryptocurrency camps, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is considered a non-negotiable feature that emerging blockchains need to support to stay relevant and attract users.
If you sort the industry’s blockchains by TVL (Total Value Locked), 9 of the top 10 networks are EVM-compatible, with Solana (SOL) being the only exception to the rule.
What exactly is the Ethereum Virtual Machine, and why is it so important?
What Is the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine)?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine is a software environment that executes code and contracts on EVM networks. An easier way to think of it is to imagine a computer’s operating system. Regardless of whether you use an HP or Lenovo laptop, it’s easy to jump between the two because you’re ultimately communicating with the device through a Windows operating system.
Let’s apply this concept to the world of blockchain technology. The Ethereum Virtual Machine means that whether you’re using Ethereum (ETH) or Polygon (MATIC), things look and feel more or less the same. For example, you don’t need to memorize the Arbitrum (ARB) whitepaper to use crypto wallets like MetaMask or a dex like Uniswap on the Arbitrum network.
If you’re confident using one EVM Chain, you’re confident using all of them.
How Does the Ethereum Virtual Machine Work?
When you look closely at the EVM, you’ll find a complex system that runs tasks consistently. The Ethereum Virtual Machine is deterministic, meaning if you give it a specific task, it will always give the same result, no matter where it’s done or who does it.
This deterministic nature is crucial for the consensus mechanism of the EVM-based networks, ensuring all nodes harmoniously agree on the state of the blockchain.
The EVM operates on a unique set of instructions, allowing for the creation, deployment, and execution of smart contracts. These contracts, written primarily in a programming language called Solidity, are then compiled into bytecode. This bytecode is what the EVM reads, interprets, and executes.
When you initiate a smart contract transaction, the EVM springs into action. It processes the transaction, calculates the necessary gas fees, and updates the blockchain’s state.
Another intriguing facet of the EVM is its Turing completeness, meaning it can perform any calculation that any other programmable computer can, provided it’s given enough time and memory.
How does this benefit the Ethereum blockchain? Well, it means that the EVM can execute any algorithm or program, granting Ethereum its iconic flexibility. This versatility helps developers create innovative smart contracts and Web 3 dApps (decentralized applications) on the Ethereum mainnet and other EVM chains.
Why Is EVM Compatibility so Important?
In an industry fraught with interoperability issues and complex bridging processes, EVM chains help to smooth the onboarding process and give users a sense of trust and familiarity with new networks.
EVM compatibility means that a blockchain can run the EVM and execute Ethereum smart contracts. This makes it easy for blockchain developers to port over existing contracts and ERC-20 tokens to a cross-chain environment and deploy crucial dApps, like decentralized exchanges or NFT marketplaces.
With the rise of multiple blockchains, each with its unique strengths like faster transactions and lower transaction fees, the ability to communicate and interact between them is of paramount importance. EVM-compatible blockchains integrate more easily than non-EVM chains, enabling assets and data to flow between different chains.
On top of that, operating an EVM helps emerging chains leverage Ethereum’s existing tools and infrastructure. Being a pioneer in the smart contract space, Ethereum has a rich ecosystem of DApps. EVM compatibility allows other blockchains to tap into this established ecosystem, benefiting from tried-and-tested tools and services without reinventing the wheel.
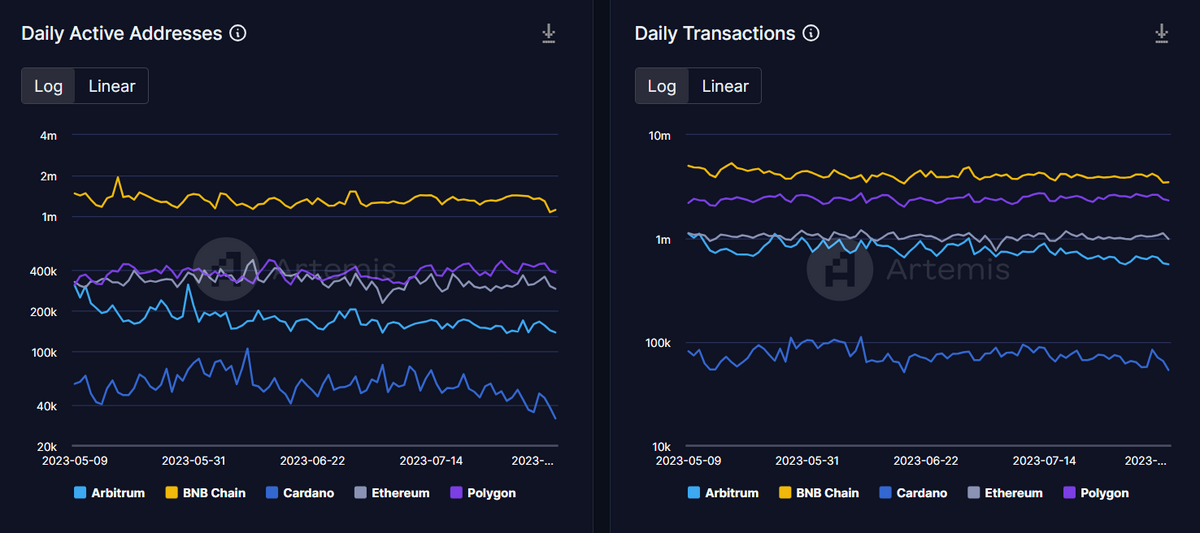
Looking at competing Layer-1 blockchains that don’t naturally support EVM compatibility, like Cardano (ADA), we see first-hand how difficult it is to onboard new users, especially in DeFi.
Despite Cardano having powerful tech in its own right, the network struggles to attract a user base as large as EVM chains like the BSC, Polygon, and Arbitrum. Cardano developers need to be proficient in the network’s dedicated programming language, Haskell, while all EVM chains use the same languages, like Solidity and Vyper.
What’s the Difference Between EVM-Equivalence and EVM-Compatibility?
Just when you thought you’d understood everything, there’s another layer of definitions. In today’s rapidly evolving industry, some blockchain ecosystems insist that simply being EVM-compatible is no longer enough. Teams like Polygon aim for EVM equivalence within the Polygon Proof-of-Stake sidechain and zkEVM.
Is there any difference between compatibility and equivalence?
EVM-Compatibility
EVM-Compatibility represents a blockchain’s ability to run the EVM and execute Ethereum-based smart contracts. An EVM-compatible blockchain can seamlessly integrate with Ethereum’s tools, protocols, and standards.
Developers can deploy the same smart contracts across multiple EVM-compatible blockchains without major code modifications.
EVM-Equivalence
On the other hand, EVM-Equivalence is a more profound alignment with the Ethereum ecosystem. An EVM-equivalent blockchain not only supports Ethereum’s smart contracts but also mirrors Ethereum’s state, account structures, and consensus mechanisms.
It’s like a twin of the Ethereum network, sharing its DNA but existing as a separate entity. EVM-equivalent blockchains can synchronize with Ethereum’s state and offer a near-identical environment for dApps and contracts.
While EVM-Compatibility offers a bridge to the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing for smooth functionality and integration, EVM-Equivalence is like walking in Ethereum’s shoes, mirroring its every step.
Examples Of EVM-Compatible Blockchains
Now that we better understand what EVM Chains are let’s dive into a quick list of the top EVM-compatible blockchains in the crypto industry.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC) – With more daily users than any other network, BNB Chain is easily the most popular EVM chain. It introduced thousands of people to DeFi for the first time and was the first major low-cost alternative to Ethereum.
- Polygon – Polygon is a multi-chain scaling solution for Ethereum-compatible blockchains building various EVM-equivalent networks.
- Avalanche (AVAX) – Another popular Layer-1 network, Avalanche is a decentralized platform tailored for custom blockchain networks and subnets.
- Arbitrum – Undoubtedly Ethereum’s most popular Layer-2 scaling solution Arbitrum boasts higher transaction throughput and lower gas fees than the Ethereum mainnet.
- Optimism (OP) – The pioneers behind ‘rollup’ technology, Optimism was one of the first Ethereum Layer-2s. On top of being EVM-compatible, Optimism has one of the most committed approaches to decentralization among EVM chains.
- Fantom (FTM) – Unlike its rivals in this list, Fantom isn’t technically a blockchain. The Fantom network is a directed acyclic graph (DAG) designed for scalability.
- Celo (CELO) – Originally designed as a simple payment network, Celo has blossomed into a fully-fledged and functional EVM chain with plenty of dApps and tools for the budding DeFi enthusiast.
EVM Chain Pros and Cons
After the invention of Bitcoin (BTC) itself, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is arguably the biggest revolution in the blockchain landscape, serving as the backbone for a myriad of decentralized applications and platforms. Of course, it’s not without its faults.
Pros
- Interoperability – EVM-compatible chains can seamlessly interact with Ethereum-based code, allowing for smooth data and asset transfers between blockchains.
- Rich Developer Ecosystem – If you can build dApps on Ethereum, you can build dApps on any EVM chain. This means native Ethereum developers can spread their knowledge throughout the wider blockchain industry.
- Standardization – EVM chains provide a standardized environment, ensuring smart contracts behave consistently across different networks.
- Security – The EVM’s isolated environment ensures that smart contracts are executed securely, protecting the network from potential vulnerabilities and external threats.
- Flexibility – The Ethereum Virtual Machine’s Turing completeness allows developers to craft intricate and versatile smart contracts, catering to various use cases and industries.
Cons
- Scalability Issues – Even on separate networks like Avalanche and BNB Chain, EVM chains are vulnerable to gas spikes and network congestion. Competing networks like Solana and XRP charge consistent transaction costs regardless of network strain.
- Complexity – While the EVM offers immense flexibility, it also introduces complexity. Developers need to be well-versed in specific programming languages like Solidity and aware of decentralized development’s nuances.
- Resource Intensity – Running and maintaining EVM nodes is resource-intensive and requires significant computational power and storage.
- Learning Curve – For newcomers, the Ethereum Virtual Machine can present a steep learning curve, marking it difficult to come to terms with.
On the Flipside
- While networks like Solana and Cardano don’t natively support EVM-based programs, independent teams have created EVM networks like NEON and Milkomeda that settle transactions on their respective Layer-1.
Why This Matters
In the current climate of the crypto industry, running an Ethereum Virtual Machine is essential if teams want to bring users to their blockchain. Without being EVM-compatible, the barriers to entry are too inconvenient.
As we can see, Cardano is a Top 10 cryptocurrency by market cap, but it has far fewer DeFi applications and TVL statistics than relatively unknown EVM-chains like Kava and Pulsechain.
FAQs
In terms of usage and on-chain metrics, the top EVM chains are Ethereum, BNB Chain, Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon.
No, Cardano is not a native EVM chain. However, Milkomeda has created an EVM-based network that settles transactions on the Cardano blockchain.
Metamask is a crypto wallet compatible with all EVM networks, including testnets. While Metamask is not an EVM chain itself, it is EVM-compatible.
Binance is a cryptocurrency exchange and trading platform, so it is technically not an EVM. That being said, the BNB Chain is an EVM-compatible network.









 All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.
All while Pfizer—a company with a $2.3 billion criminal fine for fraudulent marketing, bribery, and kickbacks—was given blanket immunity from liability and billions in taxpayer dollars to produce a vaccine in record time with no long-term safety data.